Diocese of Hereford Multi-Academy Trust
Our Family of Academies



Computing
Computing Curriculum Statement
‘I can do all things through Christ because he gives me strength.’ (Philippians 4:13 International Children’s Bible)
Achieve – The school provides an academic, physical, emotional, social and a safe environment supported by Christian values, where children are supported to engage in their learning through a broad and well-balanced curriculum so that they become confident, independent and resilient learners.
At Goodrich CE Primary, we believe that technology can transform learning. We aim to integrate technology throughout the children’s learning, giving them the necessary skills and understanding to become problem solvers, critical thinkers and enable them to be digitally literate, so that they can be responsible when using a variety of technology in new and creative ways.
|
CURRICULUM INTENT |
Curriculum Intent What a computing lesson looks like in our school:
This is our philosophy: High quality modelling and scaffolding of skills leading to…
E-Safety
This is the knowledge and understanding gained at each stage: By the end of EYFS pupils will: Children recognise that a range of technology is used in places such as homes and schools. They select and choose technology for particular purposes.
By the end of Key Stage 1 pupils will:
By the end of Key Stage 2 pupils will:
|
|
CURRICULUM IMPLEMENTATION |
Curriculum Implementation
Please refer to:
Our Computing Curriculum is carefully structured to allow pupils to develop their computational thinking and approached through a variety of activities including unplugged (without a computer), screen or physical activities. The Computing Curriculum is comprised of three key areas of study: Computer Science, Digital Literacy and Information Technology.
Computing Science Computing Science is the foundation element of the computing curriculum. In this area, pupils are encouraged to develop key computational thinking strategies such as tinkering, decomposition and debugging to ensure they become critical thinkers and apply these skills across the breadth of the curriculum. Pupils also study the hardware components and how simple networks work. During EYFS, pupils begin to write and follow algorithms, leading to programming Beebots around a maze. In Upper Key Stage 2, these skills will eventually develop into coding quizzes and using Scratch, a platform game using a block-based coding language.
Digital Literacy This element of the computing curriculum teaches pupils how to be responsible users of technology to engage and thrive in the digital world. It is at the forefront of all lessons and is embedded through PSHE, Safer Internet Day, Anti-bullying week and E-Safety lessons throughout the year. All pupils from EYFS to Year 6, are taught the knowledge and behaviours to use technology safely, so that they can be critical thinkers and be aware of who to talk to when they are upset or worried about what they have encountered on a device, app, platform etc.
Information Technology Information technology units are designed for pupils to solve problems with the aid of technology, for example, making a story come to life through animation or editing images and audio for a purpose. All pupils from EYFS to Year 6, will develop a variety of skills across different devices to enable them to make appropriate choices when deciding how to present or solve problems with the use of technology.
This is how it works:
iMovie, Garage Band, etc.
E-Safety
arise
Programming
curricular
Multimedia
Technology in our lives
learning journey and high quality teaching both overt and discrete. Apps and software include: Microsoft programs (Laptop - Word, PowerPoint, Excel), (IPad - pages, keynote, numbers), QR coding, data storage online, times table rock stars, SeeSaw, 123 Maths (Intervention), Type 2 Write, Now Press Play
Data Handling
This is what the adults do:
learning, skills and experiences
and how to keep their child safe online
This how we support pupils:
Self-assessments are used throughout the lesson, e.g. through mini-plenaries
This how we support staff:
This how we challenge children:
This how we ensure all children can access the curriculum:
Teaching lessons using a range of different techniques to suit a range of learning styles e.g. videos, interactive websites, atlases, world maps, fieldwork etc.
Cultural Capital/Enrichment What is Cultural Capital? The National Curriculum defines cultural capital as: ‘the essential knowledge that pupils need to be educated citizens, introducing them to the best that has been thought and said and helping to engender an appreciation of human creativity and achievement’. This powerful knowledge can be split into two categories: powerful subject knowledge and powerful personal knowledge. Powerful Subject Knowledge in Computing
Powerful Personal Knowledge in Computing
Cross curricular experiences to embed computing skills. |
|
CURRICULUM IMPACT |
Curriculum Impact At Goodrich Primary School, we recognise the importance of Computing in every aspect of daily life. Our Computing Curriculum facilitates sequential learning and long-term progression of knowledge and skills. Teaching and learning methods provide regular opportunities to recap acquired knowledge through high quality questioning, discussion, modelling and explaining to aid retrieval at the beginning and end of a lesson or unit. This enables all children to build on their prior knowledge and develop as computer technicians.
This is what you might typically see:
This is how we know how well our children are doing: We have identified substantive and disciplinary knowledge which is fundamental to the children’s development and understanding as computer technicians. They accumulate this as they move through our school which then gives them a firm foundation to build on when they move on to KS3 and beyond.
This is the impact of the teaching:
|
Computing Progression Document
![]() Computing Progression of Skills
Computing Progression of Skills
|
Computer Science |
Digital Literacy |
Information Technology |
||
|
Programming and Theory |
E-Safety & Research |
Communication |
Data |
Multimedia |
|
Programming Simulations Computer Theory
|
Research E-safety |
Word processing Presentations Online collaboration |
Graphs Databases Spreadsheets |
Creating images Photography Animation Video Audio |
|
Computer Science |
||||
|
Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
EYFS
Y1
|
Y1
Y2
|
Y3
Y4
|
Y4
Y5
|
Y5
Y6
Use property values and parameters to store information about objects. |
|
Digital Literacy |
|||||||
|
Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|||
|
EYFS
Y1
|
Y1
Y2
|
Y3
Y4
|
Y4
Y5
|
Y5
Lead with positivity in online communications.
Y6
|
|||
|
Information Technology |
||||
|
Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
EYFS
Y1
|
Y1
Y2
|
Y3
Y4
|
Y4
Y5
|
Y5
Y6
|
E-Safety Progression based on Project Evolve
|
Self-Image and Identity |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Recognise, online or offline, that anyone can say ‘no’ / ‘please stop’ / ‘I’ll tell’ / ‘I’ll ask’ to somebody who makes them feel sad, uncomfortable, embarrassed, or upset.
Y1 Recognise that there may be people online who could make someone feel sad, embarrassed or upset.
If something happens that makes me feel sad, worried, uncomfortable or frightened I can give examples of when and how to speak to an adult I can trust and how they can help.
|
Y1 Recognise that there may be people online who could make someone feel sad, embarrassed or upset.
If something happens that makes me feel sad, worried, uncomfortable or frightened I can give examples of when and how to speak to an adult I can trust and how they can help.
Y2 Explain how other people may look and act differently online and offline.
Give examples of issues online that might make someone feel sad, worried, uncomfortable or frightened; I can give examples of how they might get help. |
Y3 Explain what is meant by the term ‘identity’.
Explain how people can represent themselves in different ways online.
Explain ways in which someone might change their identity depending on what they are doing online (e.g. gaming; using an avatar; social media) and why. Y4 Explain how my online identity can be different to my offline identity. Describe positive ways for someone to interact with others online and understand how this will positively impact on how others perceive them. Explain that others online can pretend to be someone else, including my friends, and can suggest reasons why they might do this. |
Y4 Explain how my online identity can be different to my offline identity.
Describe positive ways for someone to interact with others online and understand how this will positively impact on how others perceive them.
Explain that others online can pretend to be someone else, including my friends, and can suggest reasons why they might do this. Y5 Explain how identity online can be copied, modified or altered.
Demonstrate how to make responsible choices about having an online identity, depending on context. |
Y5 Explain how identity online can be copied, modified or altered.
Demonstrate how to make responsible choices about having an online identity, depending on context. Y6 Identify and critically evaluate online content relating to gender, race, religion, disability, culture and other groups, and explain why it is important to challenge and reject inappropriate representations online.
Describe issues online that could make anyone feel sad, worried, uncomfortable or frightened. I know and can give examples of how to get help, both on and offline.
Explain the importance of asking until I get the help needed. |
|
Online Relationships |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Recognise some ways in which the internet can be used to communicate. Give examples of how I (might) use technology to communicate with people I know.
Y1 Give examples of when I should ask permission to do something online and explain why this is important. Use the internet with adult support to communicate with people I know (e.g. video call apps or services). Explain why it is important to be considerate and kind to people online and to respect their choices. Explain why things one person finds funny or sad online may not always be seen in the same way by others.
|
Y1 Give examples of when I should ask permission to do something online and explain why this is important. Use the internet with adult support to communicate with people I know (e.g. video call apps or services). Explain why it is important to be considerate and kind to people online and to respect their choices. Explain why things one person finds funny or sad online may not always be seen in the same way by others.
Y2 Give examples of how someone might use technology to communicate with others they don’t also know offline and explain why this might be risky. (e.g. email, online gaming, a pen-pal in another school / country). Explain who I should ask before sharing things about myself or others online. I can describe different ways to ask for, give, or deny my permission online and can identify who can help me if I am not sure. Explain why I have a right to say ‘no’ or ‘I will have to ask someone’. Explain who can help me if I feel under pressure to agree to something I am unsure about or don’t want to do. Identify who can help me if something happens online without my consent. Explain how it may make others feel if I do not ask their permission or ignore their answers before sharing something about them online.
|
Y3 Describe ways people who have similar likes and interests can get together online. Explain what it means to ‘know someone’ online and why this might be different from knowing someone offline. Explain what is meant by ‘trusting someone online’, why this is different from ‘liking someone online’, and why it is important to be careful about who to trust online including what information and content they are trusted with. Explain why someone may change their mind about trusting anyone with something if they feel nervous, uncomfortable or worried. Explain how someone’s feelings can be hurt by what is said or written online. Explain the importance of giving and gaining permission before sharing things online; how the principles of sharing online is the same as sharing offline e.g. sharing images and videos. Y4 Describe strategies for safe and fun experiences in a range of online social environments (e.g. livestreaming, gaming platforms). Give examples of how to be respectful to others online and describe how to recognise healthy and unhealthy online behaviours. Explain how content shared online may feel unimportant to one person but may be important to other people’s thoughts feelings and beliefs. |
Y4 Describe strategies for safe and fun experiences in a range of online social environments (e.g. livestreaming, gaming platforms). Give examples of how to be respectful to others online and describe how to recognise healthy and unhealthy online behaviours. Explain how content shared online may feel unimportant to one person but may be important to other people’s thoughts feelings and beliefs. Y5 Give examples of technology-specific forms of communication (e.g. emojis, memes and GIFs). Explain that there are some people I communicate with online who may want to do me or my friends harm. I can recognise that this is not my/ our fault. Describe some of the ways people may be involved in online communities and describe how they might collaborate constructively with others and make positive contributions. (e.g. gaming communities or social media groups). Explain how someone can get help if they are having problems and identify when to tell a trusted adult. Demonstrate how to support others (including those who are having difficulties) online. |
Y5 Give examples of technology-specific forms of communication (e.g. emojis, memes and GIFs). Explain that there are some people I communicate with online who may want to do me or my friends harm. I can recognise that this is not my/ our fault. Describe some of the ways people may be involved in online communities and describe how they might collaborate constructively with others and make positive contributions. (e.g. gaming communities or social media groups). Explain how someone can get help if they are having problems and identify when to tell a trusted adult. Demonstrate how to support others (including those who are having difficulties) online. Y6 Explain how sharing something online may have an impact either positively or negatively.
Describe how to be kind and show respect for others online including the importance of respecting boundaries regarding what is shared about them online and how to support them if others do not.
Describe how things shared privately online can have unintended consequences for others. e.g. screen-grabs.
Explain that taking or sharing inappropriate images of someone (e.g. embarrassing images), even if they say it is okay, may have an impact for the sharer and others; and who can help if someone is worried about this. |
|
Online Reputation |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Identify ways that I can put information on the internet.
Y1 Recognise that information can stay online and could be copied. Describe what information I should not put online without asking a trusted adult first. |
Y1 Recognise that information can stay online and could be copied. Describe what information I should not put online without asking a trusted adult first. Y2 Explain how information put online about someone can last for a long time.
Describe how anyone’s online information could be seen by others.
Know who to talk to if something has been put online without consent or if it is incorrect. |
Y3 Explain how to search for information about others online. Give examples of what anyone may or may not be willing to share about themselves online. Explain the need to be careful before sharing anything personal. Explain who someone can ask if they are unsure about putting something online. Y4 Describe how to find out information about others by searching online. Explain ways that some of the information about anyone online could have been created, copied or shared by others. Demonstrate how to support others (including those who are having difficulties) online. |
Y4 Describe how to find out information about others by searching online. Explain ways that some of the information about anyone online could have been created, copied or shared by others. Demonstrate how to support others (including those who are having difficulties) online. Y5 Search for information about an individual online and summarise the information found. Describe ways that information about anyone online can be used by others to make judgments about an individual and why these may be incorrect. |
Y5 Search for information about an individual online and summarise the information found. Describe ways that information about anyone online can be used by others to make judgments about an individual and why these may be incorrect. Y6 Explain the ways in which anyone can develop a positive online reputation.
Explain strategies anyone can use to protect their ‘digital personality’ and online reputation, including degrees of anonymity. |
|
Online Bullying |
||||
|
EYFS |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Describe ways that some people can be unkind online. Offer examples of how this can make others feel. Y1 Describe how to behave online in ways that do not upset others and can give examples.
|
Y1 Describe how to behave online in ways that do not upset others and can give examples. Y2 Explain what bullying is, how people may bully others and how bullying can make someone feel. Explain why anyone who experiences bullying is not to blame. Talk about how anyone experiencing bullying can get help. |
Y3 Describe appropriate ways to behave towards other people online and why this is important. Give examples of how bullying behaviour could appear online and how someone can get support. Y4 Recognise when someone is upset, hurt or angry online. Describe ways people can be bullied through a range of media (e.g. image, video, text, chat). Explain why people need to think carefully about how content they post might affect others, their feelings and how it may affect how others feel about them (their reputation).
|
Y4 Recognise when someone is upset, hurt or angry online. Describe ways people can be bullied through a range of media (e.g. image, video, text, chat). Explain why people need to think carefully about how content they post might affect others, their feelings and how it may affect how others feel about them (their reputation). Y5 Recognise online bullying can be different to bullying in the physical world and can describe some of those differences. Describe how what one person perceives as playful joking and teasing (including ‘banter’) might be experienced by others as bullying. Explain how anyone can get help if they are being bullied online and identify when to tell a trusted adult. Identify a range of ways to report concerns and access support both in school and at home about online bullying. Explain how to block abusive users. Describe the helpline services which can help people experiencing bullying, and how to access them (e.g. Childline or The Mix).
|
Y5 Recognise online bullying can be different to bullying in the physical world and can describe some of those differences. Describe how what one person perceives as playful joking and teasing (including ‘banter’) might be experienced by others as bullying. Explain how anyone can get help if they are being bullied online and identify when to tell a trusted adult. Identify a range of ways to report concerns and access support both in school and at home about online bullying. Explain how to block abusive users. Describe the helpline services which can help people experiencing bullying, and how to access them (e.g. Childline or The Mix). Y6 Describe how to capture bullying content as evidence (e.g screen-grab, URL, profile) to share with others who can help me. Explain how someone would report online bullying in different contexts. |
|
Managing Online Information |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Talk about how to use the internet as a way of finding information online. Identify devices I could use to access information on the internet. Y1 Give simple examples of how to find information using digital technologies, e.g. search engines, voice activated searching). Know / understand that we can encounter a range of things online including things we like and don’t like as well as things which are real or make believe / a joke. Know how to get help from a trusted adult if we see content that makes us feel sad, uncomfortable worried or frightened. |
Y1 Give simple examples of how to find information using digital technologies, e.g. search engines, voice activated searching). Know / understand that we can encounter a range of things online including things we like and don’t like as well as things which are real or make believe / a joke. Know how to get help from a trusted adult if we see content that makes us feel sad, uncomfortable worried or frightened. Y2 Use simple keywords in search engines. Demonstrate how to navigate a simple webpage to get to information I need (e.g. home, forward, back buttons; links, tabs and sections). Explain what voice activated searching is and how it might be used, and know it is not a real person (e.g. Alexa, Google Now, Siri). I can explain the difference between things that are imaginary, ‘made up’ or ‘make believe’ and things that are ‘true’ or ‘real’. Explain why some information I find online may not be real or true. |
Y3 Demonstrate how to use key phrases in search engines to gather accurate information online. Explain what autocomplete is and how to choose the best suggestion. Explain how the internet can be used to sell and buy things. I can explain the difference between a ‘belief’, an ‘opinion’ and a ‘fact and can give examples of how and where they might be shared online, e.g. in videos, memes, posts, news stories etc. Explain that not all opinions shared may be accepted as true or fair by others (e.g. monsters under the bed). Describe and demonstrate how we can get help from a trusted adult if we see content that makes us feel sad, uncomfortable worried or frightened. Y4 Analyse information to make a judgement about probable accuracy and I understand why it is important to make my own decisions regarding content and that my decisions are respected by others. Describe how to search for information within a wide group of technologies and make a judgement about the probable accuracy (e.g. social media, image sites, video sites). Describe some of the methods used to encourage people to buy things online (e.g. advertising offers; in-app purchases, pop-ups) and can recognise some of these when they appear online. Explain why lots of people sharing the same opinions or beliefs online do not make those opinions or beliefs true. Explain that technology can be designed to act like or impersonate living things (e.g. bots) and describe what the benefits and the risks might be. Explain what is meant by fake news e.g. why some people will create stories or alter photographs and put them online to pretend something is true when it isn’t. |
Y4 Analyse information to make a judgement about probable accuracy and I understand why it is important to make my own decisions regarding content and that my decisions are respected by others. Describe how to search for information within a wide group of technologies and make a judgement about the probable accuracy (e.g. social media, image sites, video sites). Describe some of the methods used to encourage people to buy things online (e.g. advertising offers; in-app purchases, pop-ups) and can recognise some of these when they appear online. Explain why lots of people sharing the same opinions or beliefs online do not make those opinions or beliefs true. Explain that technology can be designed to act like or impersonate living things (e.g. bots) and describe what the benefits and the risks might be. Explain what is meant by fake news e.g. why some people will create stories or alter photographs and put them online to pretend something is true when it isn’t. Y5 Explain the benefits and limitations of using different types of search technologies e.g. voice-activation search engine. Explain how some technology can limit the information I aim presented with e.g. voice-activated searching giving one result. Explain what is meant by ‘being sceptical’; I can give examples of when and why it is important to be ‘sceptical’. Evaluate digital content and can explain how to make choices about what is trustworthy e.g. differentiating between adverts and search results. Explain key concepts including: information, reviews, fact, opinion, belief, validity, reliability and evidence. Identify ways the internet can draw us to information for different agendas, e.g. website notifications, pop-ups, targeted ads. Describe ways of identifying when online content has been commercially sponsored or boosted, (e.g. by commercial companies or by vloggers, content creators, influencers). Explain what is meant by the term ‘stereotype’, how ‘stereotypes’ are amplified and reinforced online, and why accepting ‘stereotypes’ may influence how people think about others. Describe how fake news may affect someone’s emotions and behaviour, and explain why this may be harmful. Explain what is meant by a ‘hoax’. I can explain why someone would need to think carefully before they share.
|
Y5 Explain the benefits and limitations of using different types of search technologies e.g. voice-activation search engine. Explain how some technology can limit the information I aim presented with e.g. voice-activated searching giving one result. Explain what is meant by ‘being sceptical’; I can give examples of when and why it is important to be ‘sceptical’. Evaluate digital content and can explain how to make choices about what is trustworthy e.g. differentiating between adverts and search results. Explain key concepts including: information, reviews, fact, opinion, belief, validity, reliability and evidence. Identify ways the internet can draw us to information for different agendas, e.g. website notifications, pop-ups, targeted ads. Describe ways of identifying when online content has been commercially sponsored or boosted, (e.g. by commercial companies or by vloggers, content creators, influencers). Explain what is meant by the term ‘stereotype’, how ‘stereotypes’ are amplified and reinforced online, and why accepting ‘stereotypes’ may influence how people think about others. Describe how fake news may affect someone’s emotions and behaviour, and explain why this may be harmful. Explain what is meant by a ‘hoax’. I can explain why someone would need to think carefully before they share. Y6 Explain how search engines work and how results are selected and ranked. Explain how to use search technologies effectively. Describe how some online information can be opinion and can offer examples. Explain how and why some people may present ‘opinions’ as ‘facts’. Explain why the popularity of an opinion or the personalities of those promoting it does not necessarily make it true, fair or perhaps even legal. Define the terms ‘influence’, ‘manipulation’ and ‘persuasion’ and explain how someone might encounter these online (e.g. advertising and ‘ad targeting’ and targeting for fake news). Understand the concept of persuasive design and how it can be used to influences peoples’ choices. Demonstrate how to analyse and evaluate the validity of ‘facts’ and information and I can explain why using these strategies are important. Explain how companies and news providers target people with online news stories they are more likely to engage with and how to recognise this. Describe the difference between online misinformation and dis-information. Explain why information that is on a large number of sites may still be inaccurate or untrue. I can assess how this might happen (e.g. the sharing of misinformation or disinformation). Identify, flag and report inappropriate content. |
|
Health, Well-bring and Lifestyle |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Identify rules that help keep us safe and healthy in and beyond the home when using technology. Give some simple examples of these rules. Y1 Explain rules to keep myself safe when using technology both in and beyond the home.
|
Y1 Explain rules to keep myself safe when using technology both in and beyond the home. Y2 Explain simple guidance for using technology in different environments and settings e.g. accessing online technologies in public places and the home environment. Say how those rules / guides can help anyone accessing online technologies.
|
Y3 Explain why spending too much time using technology can sometimes have a negative impact on anyone, e.g. mood, sleep, body, relationships; Give some examples of both positive and negative activities where it is easy to spend a lot of time engaged (e.g. doing homework, games, films, videos). Explain why some online activities have age restrictions, why it is important to follow them and know who I can talk to if others pressure me to watch or do something online that makes me feel uncomfortable (e.g. age restricted gaming or web sites). Y4 Explain how using technology can be a distraction from other things, in both a positive and negative way. Identify times or situations when someone may need to limit the amount of time they use technology e.g. I can suggest strategies to help with limiting this time.
|
Y4 Explain how using technology can be a distraction from other things, in both a positive and negative way. Identify times or situations when someone may need to limit the amount of time they use technology e.g. I can suggest strategies to help with limiting this time. Y5 Describe ways technology can affect health and wellbeing both positively (e.g. mindfulness apps) and negatively. Describe some strategies, tips or advice to promote health and well-being with regards to technology. Recognise the benefits and risks of accessing information about health and well-being online and how we should balance this with talking to trusted adults and professionals. Explain how and why some apps and games may request or take payment for additional content (e.g. inapp purchases, lootboxes) and explain the importance of seeking permission from a trusted adult before purchasing.
|
Y5 Describe ways technology can affect health and wellbeing both positively (e.g. mindfulness apps) and negatively. Describe some strategies, tips or advice to promote health and well-being with regards to technology. Recognise the benefits and risks of accessing information about health and well-being online and how we should balance this with talking to trusted adults and professionals. Explain how and why some apps and games may request or take payment for additional content (e.g. inapp purchases, lootboxes) and explain the importance of seeking permission from a trusted adult before purchasing. Y6 Describe common systems that regulate age-related content (e.g. PEGI, BBFC, parental warnings) and describe their purpose. Recognise and can discuss the pressures that technology can place on someone and how / when they could manage this. Recognise features of persuasive design and how they are used to keep users engaged (current and future use). Assess and action different strategies to limit the impact of technology on health (e.g. night-shift mode, regular breaks, correct posture, sleep, diet and exercise). |
|
Privacy and Security |
||||
|
EYFS- Wrens |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Identify some simple examples of my personal information (e.g. name, address, birthday, age, location). Describe who would be trustworthy to share this information with; I can explain why they are trusted. Y1 Explain that passwords are used to protect information, accounts and devices. Recognise more detailed examples of information that is personal to someone (e.g where someone lives and goes to school, family names). Explain why it is important to always ask a trusted adult before sharing any personal information online, belonging to myself or others. |
Y1 Explain that passwords are used to protect information, accounts and devices. Recognise more detailed examples of information that is personal to someone (e.g where someone lives and goes to school, family names). Explain why it is important to always ask a trusted adult before sharing any personal information online, belonging to myself or others. Y2 Explain how passwords can be used to protect information, accounts and devices. I can explain and give examples of what is meant by ‘private’ and ‘keeping things private’. Describe and explain some rules for keeping personal information private (e.g. creating and protecting passwords). Explain how some people may have devices in their homes connected to the internet and give examples (e.g. lights, fridges, toys, televisions).
|
Y3 Explain why spending too much time using technology can sometimes have a negative impact on anyone, e.g. mood, sleep, body, relationships; Give some examples of both positive and negative activities where it is easy to spend a lot of time engaged (e.g. doing homework, games, films, videos). Explain why some online activities have age restrictions, why it is important to follow them and know who I can talk to if others pressure me to watch or do something online that makes me feel uncomfortable (e.g. age restricted gaming or web sites). Y4 Describe strategies for keeping personal information private, depending on context. Explain that internet use is never fully private and is monitored, e.g. adult supervision. Describe how some online services may seek consent to store information about me; I know how to respond appropriately and who I can ask if I am not sure. Know what the digital age of consent is and the impact this has on online services asking for consent. |
Y4 Describe strategies for keeping personal information private, depending on context. Explain that internet use is never fully private and is monitored, e.g. adult supervision. Describe how some online services may seek consent to store information about me; I know how to respond appropriately and who I can ask if I am not sure. Know what the digital age of consent is and the impact this has on online services asking for consent. Y5 Explain what a strong password is and demonstrate how to create one. Explain how many free apps or services may read and share private information (e.g. friends, contacts, likes, images, videos, voice, messages, geolocation) with others. Explain what app permissions are and can give some examples.
|
Y5 Explain what a strong password is and demonstrate how to create one. Explain how many free apps or services may read and share private information (e.g. friends, contacts, likes, images, videos, voice, messages, geolocation) with others. Explain what app permissions are and can give some examples. Y6 Describe effective ways people can manage passwords (e.g. storing them securely or saving them in the browser). Explain what to do if a password is shared, lost or stolen. Describe how and why people should keep their software and apps up to date, e.g. auto updates. Describe simple ways to increase privacy on apps and services that provide privacy settings. Describe ways in which some online content targets people to gain money or information illegally; I can describe strategies to help me identify such content (e.g. scams, phishing). Know that online services have terms and conditions that govern their use. Assess and action different strategies to limit the impact of technology on health (e.g. night-shift mode, regular breaks, correct posture, sleep, diet and exercise). |
|
Copyright and Ownership |
||||
|
EYFS |
Robins |
Woodpeckers |
Owls |
Peregrines |
|
Know that work I create belongs to me. Name my work so that others know it belongs to me. Y1 Explain why work I create using technology belongs to me. Say why it belongs to me (e.g. ‘I designed it’ or ‘I filmed it’’). Save my work under a suitable title / name so that others know it belongs to me (e.g. filename, name on content). Understand that work created by others does not belong to me even if I save a copy. |
Y1 Explain why work I create using technology belongs to me. Say why it belongs to me (e.g. ‘I designed it’ or ‘I filmed it’’). Save my work under a suitable title / name so that others know it belongs to me (e.g. filename, name on content). Understand that work created by others does not belong to me even if I save a copy. Y2 Recognise that content on the internet may belong to other people. Describe why other people’s work belongs to them.
|
Y3 Explain why copying someone else’s work from the internet without permission isn’t fair and can explain what problems this might cause. Y4 When searching on the internet for content to use, I can explain why I need to consider who owns it and whether I have the right to reuse it. Give some simple examples of content which I must not use without permission from the owner, e.g. videos, music, images.
|
Y4 When searching on the internet for content to use, I can explain why I need to consider who owns it and whether I have the right to reuse it. Give some simple examples of content which I must not use without permission from the owner, e.g. videos, music, images. Y5 Assess and justify when it is acceptable to use the work of others. Give examples of content that is permitted to be reused and know how this content can be found online. |
Y5 Assess and justify when it is acceptable to use the work of others. Give examples of content that is permitted to be reused and know how this content can be found online. Y6 Demonstrate the use of search tools to find and access online content which can be reused by others. Demonstrate how to make references to and acknowledge sources I have used from the internet. |
Computing Sticky Knowledge
|
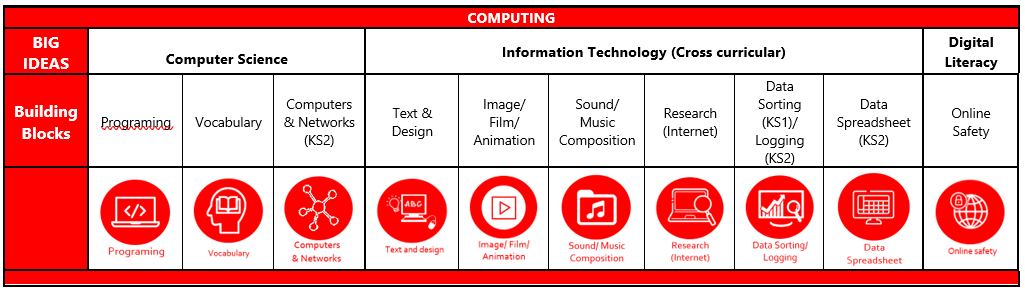
COMPUTING |
||||||||||
|
BIG IDEAS |
Computer Science (Taught discreetly) |
Information Technology (Cross curricular) |
Digital Literacy |
|||||||
|
Building Blocks |
Programming |
Vocabulary |
Computers & Networks |
Text & Design |
Image/ Film/ Animation |
Sound/ Music Composition |
Research (Internet) |
Data Sorting (KS1)/ Logging (KS2) |
Data Spreadsheet (KS2) |
Online Safety |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
Computer Science |
Information Technology |
Digital Literacy |
||||||
|
Class |
Programming |
Vocabulary |
Computer & Networks (KS2) |
Text & Design |
Image/Film/Animation |
Sound/Music Composition |
Research (Internet) |
Data Sorting (KS1)/logging (KS2) Data Spreadsheet (KS2) |
Online Safety |
|
Wrens: Reception (EYFS) Year 1 |
Follow a set of instructions to move forwards, backwards and to make turns. ( Unplugged) Know how to make a beebot to move 1 and then 2 steps forwards / backwards. Be able to make an icon move forward 5 steps and back 5 steps. Know that an algorithm is a list of steps. Know the 4 commands for the Beebot and use in a sequence including forwards/ backwards. Explain what a start block does in a program. Name directional blocks which move a sprite. |
Children are able to use the list of vocabulary in their explanation and understand the different terms used in their lessons. |
Name a type of technology in the classroom. Name a type of technology in our school. Locate a mouse, keyboard and monitor on a desktop computer. Name 3 types of technology. Locate the on switch of a desktop PC. Know that the shift key creates a capital letter. |
Use a device to interact with age appropriate apps e.g . using Draw and Tell app. Know how to use a mouse to make lines and squiggles. Know the icons for the shape and line tools to draw a picture. Explain how to change the colour and size of the paintbrush. Know that the space keys make a space and backspace deletes text. Know where the font and size icons are and that they change font size and make the text bigger or smaller. |
Use technology to take photos/films. |
Use technology to listen to music.
Use technology to make music. |
Use a QR code to engage with a website. Know that they can use technology to find information online.
|
To know how to read a simple block graph. To name a group of objects using a label according to property ( including size, shape or colour.)
|
To recognise kind and unkind behaviour. To be able to identify the positives and negatives when using technology. To understand how your online activity can affect others. |
|
Robins Years 1/2 |
Know the 4 commands for the Beebot and use in a asequence including forwards/ backwards. Explain what a start block does in a program. Name directional blocks which move a sprite. Write a program for the Beebot using the 4 commands in a sequence including forwards/ backwards/ left turn/ right turn. Know when and how to debug programs. Know a series of instructions (usually on a computer) is called an algorithm. Be able to move the sprite and manipulate the controls by setting conditions. E.g. Jump high. Change the background on Scratch. Create 2 sprites and make a conversation happen between them. Know how to save and retrieve projects. Say one way a project could be improved. |
Children are able to use the list of vocabulary in their explanation and understand the different terms used in their lessons. |
Name 3 types of technology. Locate the on switch of a desktop PC. Know that the shift key creates a capital letter. Know that if something online is upsetting, it needs to be reported to an adult.
Name examples of how IT helps to improve our word. e.g. traffic lights and how they keep us safe on the road. |
Know the icons for the shape and line tools to draw a picture. Explain how to change the colour and size of the paintbrush. Know that the space keys make a space and backspace deletes text. Know where the font and size icons are and that they change font size and make the text bigger or smaller. Be able to add text and an image. Be able to save and retrieve work. Explain how we can present information using a computer. |
Explain how you can take/capture a digital photo.
Describe how some tools can be used to change an image.
Identify which photos are real and which have been changed.
|
Show how music is made from a series of notes. Show how you can create a rhythm pattern on a computer/device and how it can be changed.
Show how you can change pitch on a computer/device.
|
Be able to use a scroll bar on webpages.
|
To name a group of objects using a label according to property (including size, shape or colour.) To understand, use and read a tally chart. To use a program to create a pictogram.
|
To be able to identify the positives and negatives when using technology. To understand how your online activity can affect others. To know the risks of sharing information without permission To understand the type of information you should/should not share online. |
|
Woodpeckers Years 3/4 |
Explain what a sprite is. Be able to identify sprites and backgrounds in the Scratch program. Know that event blocks are yellow and movement blocks are darker blue on Scratch. Be able to identify patterns of repetition in real life. ( brushing teeth, dance) Explain how to use the repeat blocks in Scratch. Be able to explain the uses of repetition in programming and link this with the drawing of various shapes. |
Children are able to use the list of vocabulary in their explanation and understand the different terms used in their lessons. |
Identify at least 2 networked devices around them, ( Network switch, server, Wire- less Access Point WAP) Be able to explain that different devices have different purposes. Know that websites and their content are created by people. Know that information found online is not necessarily honest, accurate or legal. Know what a URL address is and how to access a website.
|
Explain the difference between text and images. Be able to demonstrate how to change font size and colour on a document.
|
Be able to explain that an animation is a sequence of pictures or images. Be able to name a program used to make stop, frame animation, (e.g. iMotion). Explain the term ‘onion skinning’ when used to create an animation.
Explain/show how you can add other media to an animation.
Explain some ways in how you can edit a photo.
|
Identify the uses for recorded audio ( music , podcasts etc.) Explain the ways that audio can be recorded and how to make it of high quality.
|
Be able to use the internet to gather research for cross curricular subjects.
Be able to copy and save images from the internet. |
To give an example of an open-ended question and a yes/ no question. To know that the objects in a branching data- base need to be split into similar sized groups. To be able to explain the reasons why somebody may want to change the composition of an image. To be able to give examples of positive and negative effects that editing an image may have. Be able to explain the uses for gathered data. Be able to explain the different ways data might be gathered.
|
To understand the difference between safe and risky choices online. To know why passwords are important. To recognise the key values that are important in positive online relationships. To identify how and who to ask for help. |
|
Owls Years 4/5 |
Be able to identify patterns of repetition in real life. ( brushing teeth, dance) Explain how to use the repeat blocks in Scratch. Be able to explain the uses of repetition in programming and link this with the drawing of various shapes. Know that a loop can be stopped when a condition is met. Explain a loop can be used to repeatedly check when a condition has been met (or not). Explain how selection is used in computer pro- grams. Explain how selection effects the flow of a program. |
Children are able to use the list of vocabulary in their explanation and understand the different terms used in their lessons. |
Know that websites and their content are created by people. Know that information found online is not necessarily honest, accurate or legal. Know what a URL address is and how to access a website. Describe that a computer system uses an input, process and an output. Explain that different media, files and information can be shared on the internet either privately or publicly. Explain how the internet enables effective collabo- ration. |
Know that vector drawing has different layers / shapes. Know drawing tools can be used to produce different outcomes.
|
Explain/show how you can add other media to an animation.
Explain some ways in how you can edit a photo.
Recognise videos are moving images which may include sound. Name digital devices that can record video. Identify what makes an effective / appealing video.
|
Identify the uses for recorded audio ( music , podcasts etc.) Explain the ways that audio can be recorded and how to make it of high quality.
|
Be able to use the internet to gather research for cross curricular subjects.
Be able to copy and save images from the internet. |
To be able to explain the reasons why somebody may want to change the composition of an image. To be able to give examples of positive and negative effects that editing an image may have. Can explain that programs can be used to compare data. Can explain how information can be grouped. Can explain what a ‘field’ and ‘record’ in a database.
Be able to explain the uses for gathered data. Be able to explain the different ways data might be gathered.
|
To recognise the key values that are important in positive online relationships. To identify how and who to ask for help.
To recognise possible influences and pressures that may present themselves online
To know when to act upon negative online behaviours. |
|
Peregrines Years 5/6 |
Know that a loop can be stopped when a condition is met. Explain a loop can be used to repeatedly check when a condition has been met (or not). Explain how selection is used in computer pro- grams. Explain how selection effects the flow of a program. Define a ‘variable’ as something changeable. Explain why a variable is used in a program. Explain that some devices need to have sensors in order to help it make decisions about how many jumps have been made. Explain that what a device senses can change the flow of a program. |
Children are able to use the list of vocabulary in their explanation and understand the different terms used in their lessons. |
Describe that a computer system uses an input, process and an output. Explain that different media, files and information can be shared on the internet either privately or publicly. Explain how the internet enables effective collabo- ration. Explain that search results are ordered. Name a variety of ways of communicating over the internet, (email, social media post, comment field, blog, vlog etc.) |
Know that vector drawing has different layers / shapes. Know drawing tools can be used to produce different outcomes. Name 3D shapes needed to create a model of a real world objects. Explain why we might represent 3D objects on a computer. Use a range of different programmes to present work. Name the common features of a webpage.
|
Recognise videos are moving images which may include sound. Name digital devices that can record video. Identify what makes an effective / appealing video.
|
Use programmes/apps to create music e.g. GarageBand.
|
Define what is meant by the terms, ‘copyright’ and ‘fair use’. Describe how pages of a website are linked together (through the use of hyperlinks). Explain what a navigation path is and why it might be useful when creating a webpage. Use the internet to help with research for cross curricular subjects. Be able to copy and save images from the internet.
|
Can explain that programs can be used to compare data. Can explain how information can be grouped. Can explain what a ‘field’ and ‘record’ in a database. Can explain that objects can be described using data. Knows that a formula must start with an = sign. Knows that data an be best represented in tables or graphs. |
To recognise possible influences and pressures that may present themselves online
To know when to act upon negative online behaviours. To understand the relationship between online and offline behaviours and their impact on myself and others. To understand and be able to name healthy strategies when using technology and going online
|
Computing Vocabulary
|
Wrens Year A & B |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Technology around us
technology computer mouse trackpad keyboard screen double-click typing |
Programming - Moving a robot
Bee-Bot forwards backwards turn clear go commands instructions directions left right route plan algorithm program
|
Creating media - Digital painting
paint program tool paintbrush erase fill undo shape tools line tool fill tool undo tool colour brush style brush size pictures painting computers
|
Data and information – Grouping
object label group search image property colour size shape value data set more less most fewest least the same
|
Programming animations
Scratch Junior command sprite compare programming area block joining start run program background delete reset algorithm predict effect change value instructions design
|
Creating media - Digital writing
word processor keyboard keys letters type numbers space backspace text cursor capital letters toolbar bold italic underline mouse select font undo redo format compare typing writing |
|
Robins Year A |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Information technology around us
Information technology (IT) computer Barcode scanner/scan
|
Robot Algorithms
instruction sequence clear unambiguous algorithm program order prediction artwork design route mat debugging decomposition
|
Creating media - Digital Photography
device camera photograph capture image digital landscape portrait framing subject compose light sources flash focus background editing filter format lighting
|
Data and information – Pictograms
more than less than most least common popular organise data object tally chart votes total pictogram enter data compare objects count explain attribute group same different conclusion block diagram sharing
|
Programming quizzes
sequence command program run start outcome predict blocks design actions sprite project modify change algorithm build match compare debug features evaluate decomposition code
|
Creating media - Digital Music
music quiet loud feelings emotions pattern rhythm pulse pitch tempo rhythm notes create emotion beat instrument open edit
|
|
Robins Year B |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Technology around us
technology computer mouse trackpad keyboard screen double-click typing |
Programming - Moving a robot
Bee-Bot forwards backwards turn clear go commands instructions directions left right route plan algorithm program
|
Creating media - Digital painting
paint program tool paintbrush erase fill undo shape tools line tool fill tool undo tool colour brush style brush size pictures painting computers
|
Data and information – Grouping
object label group search image property colour size shape value data set more less most fewest least the same
|
Programming animations
ScratchJr command sprite compare programming area block joining start run program background delete reset algorithm predict effect change value instructions design
|
Creating media - Digital writing
word processor keyboard keys letters type numbers space backspace text cursor capital letters toolbar bold italic underline mouse select font undo redo format compare typing writing |
|
Woodpeckers Year A |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Connecting Computers
digital device input process output program digital non-digital connection network switch server wireless access point cables sockets
|
Sequencing Sounds
Scratch programming blocks commands code sprite costume stage backdrop motion turn point in direction go to glide sequence event task design run the code order note chord algorithm bug debug code
|
Stop-Frame Animation
animation flip book stop- frame frame sequence image photograph setting character events onion skinning consistency evaluation delete media import transition
|
Branching databases
attribute value questions table objects branching database objects equal even separate structure compare order organise selecting information decision tree
|
Repetition in Shapes
Logo (programming environment) program turtle commands code snippet algorithm design debug pattern repeat repetition count-controlled loop value trace decompose procedure
|
Desktop publishing
text images advantages disadvantages communicate font style landscape portrait orientation placeholder template layout content desktop publishing copy paste purpose benefits
|
|
Woodpeckers Year B |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
The Internet
internet network router security switch server wireless access point (WAP) website web page web address routing web browser World Wide Web content links files use download sharing ownership permission information accurate honest content adverts
|
Events & Actions in Programs
motion event sprite algorithm logic move resize extension block pen up set up pen design action debugging errors setup code test debug actions
|
Photo Editing
image edit digital crop rotate undo save adjustments effects colours hue saturation sepia vignette image retouch clone select combine made up real composite cut copy paste alter background foreground zoom undo font |
Data Logging
data table layout input device sensor logger logging data point interval analyse dataset import export logged collection review conclusion
|
Repetition in Games
Scratch programming sprite blocks code loop repeat value infinite loop count-controlled loop costume repetition forever animate event block duplicate modify design algorithm debug refine evaluate
|
Audio Production
audio microphone speaker headphones input device output device sound podcast edit trim align layer import record playback selection load save export MP3 evaluate feedback
|
|
Owls Year A |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Systems and Searching
system connection digital input process storage output search search engine refine index bot ordering links algorithm search engine optimisation (SEO) web crawler content creator selection ranking
|
Selection in Physical Computing
microcontroller USB components connection infinite loop output component motor repetition count-controlled loop Crumble controller switch LED Sparkle crocodile clips connect battery box program condition Input output selection action debug circuit power cell buzzer
|
Video Production
video audio camera talking head panning close up video camera microphone lens mid-range long shot moving subject side by side angle (high, low) normal static zoom pan tilt storyboard filming review import split trim clip edit reshoot delete reorder export evaluate share
|
Flat-file Databases
database data information record field sort order group search value criteria graph chart axis compare filter presentation
|
Repetition in Shapes
Logo (programming environment) program turtle commands code snippet algorithm design debug pattern repeat repetition count-controlled loop value trace decompose procedure
|
Vector Graphics
vector drawing tools object toolbar vector drawing move resize colour rotate duplicate/copy zoom select align modify layers order copy paste group ungroup reuse reflection
|
|
Owls Year B |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
The Internet
internet network router security switch server wireless access point (WAP) website web page web address routing web browser World Wide Web content links files use download sharing ownership permission information accurate honest content adverts
|
Making Quizzes
Selection, condition, true, false, count-controlled loop, outcomes, conditional statement, algorithm, program, debug, question, answer, task, design, input, implement, test, run, setup, operator
|
Photo Editing
image edit digital crop rotate undo save adjustments effects colours hue saturation sepia vignette image retouch clone select combine made up real composite cut copy paste alter background foreground zoom undo font |
Data Logging
data table layout input device sensor logger logging data point interval analyse dataset import export logged collection review conclusion
|
Repetition in Games
Scratch programming sprite blocks code loop repeat value infinite loop count-controlled loop costume repetition forever animate event block duplicate modify design algorithm debug refine evaluate
|
Audio Production
audio microphone speaker headphones input device output device sound podcast edit trim align layer import record playback selection load save export MP3 evaluate feedback
|
|
Peregrines Year A |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Systems and Searching
system connection digital input process storage output search search engine refine index bot ordering links algorithm search engine optimisation (SEO) web crawler content creator selection ranking
|
Selection in Physical Computing
microcontroller USB components connection infinite loop output component motor repetition count-controlled loop Crumble controller switch LED Sparkle crocodile clips connect battery box program condition Input output selection action debug circuit power cell buzzer
|
Webpage Creation website web page browser media Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) logo layout header media purpose copyright fair use home page preview evaluate device Google Sites breadcrumb trail navigation hyperlink subpage evaluate implication external link embed
|
Spreadsheets data collecting table structure spreadsheet cell cell reference data item format formula calculation spreadsheet input output operation range duplicate sigma propose question data set organised chart evaluate results sum comparison software tools
|
Sensing (Programming) Micro:bit MakeCode input process output flashing USB trace selection condition if then else variable random sensing accelerometer value compass direction navigation design task algorithm step counter plan create code test debug
|
3D Modelling TinkerCAD 2-dimensonal (2D) 3-dimensonal (3D) shapes select move perspective view handles resize lift lower recolour rotate duplicate group cylinder cube cuboid sphere cone prism pyramid placeholder hollow choose combine construct evaluate modify
|
|
Peregrines Year B |
|||||
|
Autumn |
Spring |
Summer |
|||
|
Communication communication protocol data address Internet Protocol (IP) Domain Name Server (DNS) Packet Header data payload chat explore slide deck reuse remix collaboration internet public private one-way two-way one-to-one one-to-many
|
Variables in Games variable, change name value set design event algorithm code task artwork program project code test debug improve evaluate share assign declare
|
Video Production
video audio camera talking head panning close up video camera microphone lens mid-range long shot moving subject side by side angle (high, low) normal static zoom pan tilt storyboard filming review import split trim clip edit reshoot delete reorder export evaluate share
|
Flat-file Databases
database data information record field sort order group search value criteria graph chart axis compare filter presentation
|
Making Quizzes
Selection condition true false count-controlled loop outcomes conditional statement algorithm program debug question answer task design input implement test run setup operator |
Vector Graphics
vector drawing tools object toolbar vector drawing move resize colour rotate duplicate/copy zoom select align modify layers order copy paste group ungroup reuse reflection
|
Computing Recommended Reads/ Websites/ Apps
Digital Literacy (Internet Safety)
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Computer Science (Programming and Coding)
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Other Recommended Reads for Computing
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Recommended Websites
Homepage - UK Safer Internet Centre
Be Internet Legends - A Program to Teach Children Internet Safety (beinternetawesome.withgoogle.com)
Dance Mat Typing for 7 - 11 year olds - BBC Bitesize
Chrome Music Lab (chromeexperiments.com)
Scratch - Imagine, Program, Share (mit.edu)
Welcome to the Minecraft Official Site | Minecraft
Primary computing resource collections (stem.org.uk)
Projects | Computer coding for kids and teens | Raspberry Pi
FIRST LEGO League – teachictnt.org.uk
Micro:bit Educational Foundation | micro:bit (microbit.org)
Online Safety Information/Websites for Parents
| Pegi Public Site (Guide to Gaming)
Keeping children safe online | NSPCC
Recommended Apps





GoodrichChurch of England Primary School
Contact Us
Ross-on-Wye, Herefordshire, HR9 6HY