Diocese of Hereford Multi-Academy Trust
Our Family of Academies


Science
Science Curriculum Statement
‘As the children move through the school, they blossom as they grow as unique individuals, benefitting from the strength and faith of our school.’ – ref. School Vision
What Science looks like in Goodrich CE Primary School
We aim to use Science to stimulate and excite children's curiosity about phenomena and events in the world around them as well as giving them the opportunities to develop their understanding and increase their knowledge. We aim to promote the development of enquiry, exploration and observation in a meaningful context. Science lessons encourage children to work collaboratively and independently to learn about the world around them.
|
CURRICULUM INTENT |
Curriculum Intent What a Science looks like in our school.
This is our philosophy:
|
|
CURRICULUM INTENT |
This is the knowledge and understanding gained at each stage:
By the end of EYFS pupils will:
By the end of Key Stage 1 pupils will:
By the end of Key Stage 2 pupils will:
|
|
CURRICULUM IMPLEMENTATION |
Curriculum Implementation
Please refer to:
This is how it works:
This is what the adults do:
This is how we support children:
This is how we support staff:
This is how we challenge:
This is how we ensure all children can access the curriculum:
Cultural Capital/Enrichment
In addition, the intent behind science is to contribute towards the cultural capital for the children in terms of the knowledge and skills they need to be successful learners and in wider life. Cultural capital in science has been identified in terms of the knowledge useful to our lives. We are aware that powerful knowledge will put children at an advantage.
The powerful knowledge we teach in science is as follows:
|
|
CURRICULUM IMPACT |
Curriculum Impact At Goodrich Primary School, we recognise the importance of science in every aspect of daily life. Our Science Curriculum facilitates sequential cyclical learning and long-term progression of knowledge and skills. Teaching and learning methods provide regular opportunities to recap acquired knowledge through high quality questioning, discussion, modelling and explaining to aid retrieval at the beginning and end of a lesson or unit. This enables all children to build on their prior knowledge and develop as Scientists.
This is what you might typically see:
This is how we know how well our children are doing: We have identified substantive and disciplinary knowledge which is fundamental to the children’s development and understanding as scientists. They accumulate this as they move through our school which then gives them a firm foundation to build on when they move on to KS3 and beyond.
This is the impact of the teaching:
|
Science Progression Document
|
Topic |
Page |
Classes |
|
Enquiry Approaches |
3-4 |
All |
|
Plants |
4-7 |
Wrens, Robins and Woodpeckers |
|
Animals, including Humans |
5-17 |
All |
|
Evolution and inheritance |
18-19 |
Peregrines |
|
Living things and their habitats |
20-27 |
All |
|
Electricity |
28-31 |
Owls and Peregrines |
|
Forces |
32-35 |
Woodpeckers and Owls |
|
Earth and space |
36-37 |
Owls |
|
Energy (Seasons, Light and Sound) |
38-44 |
Wrens, Robins, Woodpeckers and Peregrines |
|
Materials |
45-55 |
All |
|
Enquiry Approaches used to teach |
|||||
|
Comparative test |
Identify and Classify |
Observation over time |
Pattern seeking |
Research |
Problem solving assessment opportunities |
Overview KS1 (Milestone 1)
|
SCIENCE |
Each Year (Special Days) |
Year A |
Year B |
|
AUTUMN 1 |
Seasonal change |
Materials |
Plants |
|
AUTUMN 2 |
Seasonal change |
Seasonal Change |
Seasonal Change |
|
SPRING 1 |
Seasonal change Science Week |
Animals including humans |
Materials |
|
SPRING 2 |
Seasonal change |
Plants |
Animals including humans |
|
SUMMER 1 |
Seasonal change |
Living things and their habitats |
Living things and their habitats |
|
SUMMER 2 |
Seasonal change |
Awe and Wonder Famous scientist |
Awe and Wonder Famous scientist |
Overview WOODPECKERS KS2- Years 3&4 (Milestone 2)
| SCIENCE | Each Year (special days) | Year A | Year B | ||
|
AUTUMN 1 |
|
Animals including humans |
Animals including humans |
||
|
AUTUMN 2 |
|
Light and Sound |
Light and Sound |
||
|
SPRING 1 |
Science Week |
Forces and Magnets |
Materials - Rocks |
||
|
SPRING 2 |
|
Plants |
Plants |
||
|
SUMMER 1 |
|
Materials - Rocks |
Living things and their habitats |
||
|
SUMMER 2 |
|
Living things and their habitats |
Forces and Magnets |
||
Overview OWLS KS2- Years 4&5 (Milestone 2/3)
| SCIENCE | Each year (special days) | Year A | Year B | ||
|
AUTUMN 1 |
|
Animals including humans |
Earth and Space |
||
|
AUTUMN 2 |
|
Electricity |
Electricity |
||
|
SPRING 1 |
Science Week |
Forces |
Forces |
||
|
SPRING 2 |
|
Earth and Space |
Animals including humans |
||
|
SUMMER 1 |
|
Materials -State of Matter |
Living things and their habitats |
||
|
SUMMER 2 |
|
Living things and their habitats |
Materials – State of Matter |
||
Overview PEREGRINES KS2- Years 5&6 (Milestone 3)
| SCIENCE | Each year (special days) | Year A | Year B | ||
|
AUTUMN 1 |
|
Materials – Mixture, separation and change |
Materials – Mixture, separation and change |
||
|
AUTUMN 2 |
|
Animals including humans |
Animals including humans |
||
|
SPRING 1 |
Science Week |
Light and Sound |
Light and Sound |
||
|
SPRING 2 |
|
Electricity |
Electricity |
||
|
SUMMER 1 |
|
Living things and their habitats |
Living things and their habitats |
||
|
SUMMER 2 |
|
Evolution and Inheritance |
Evolution and Inheritance |
||
Science Assessment
Science: Assessment and Essential Building Blocks
Children are assessed within lessons on a regular basis. Frequent opportunities are built into lessons to assess children’s retention of previous objectives taught to ensure that the objectives are securely achieved.
Progress through objectives are recorded on data sheets termly. Analysis of this data is completed shortly after each data point and used to inform teaching and learning.
Evidence for assessment could also include:
- Children’s work
- Marking codes and annotations
- Teacher/TA observation notes
- Photographs with annotations
- Audio recordings
- End of unit tasks
Essential Building Blocks
In Early Year Science is assessed using teacher assessment based on the Birth to 5 Matters criteria.
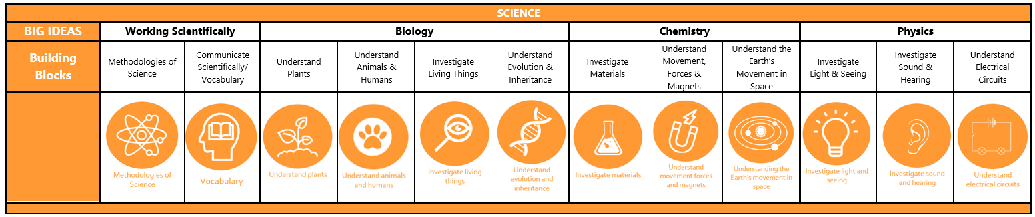
Essential Building Blocks for Year 1
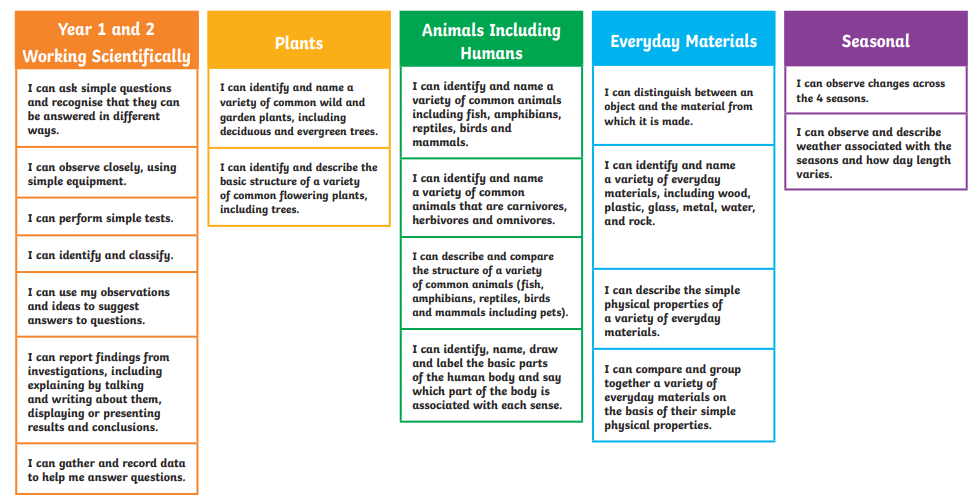
Essential Building Blocks for Year 2
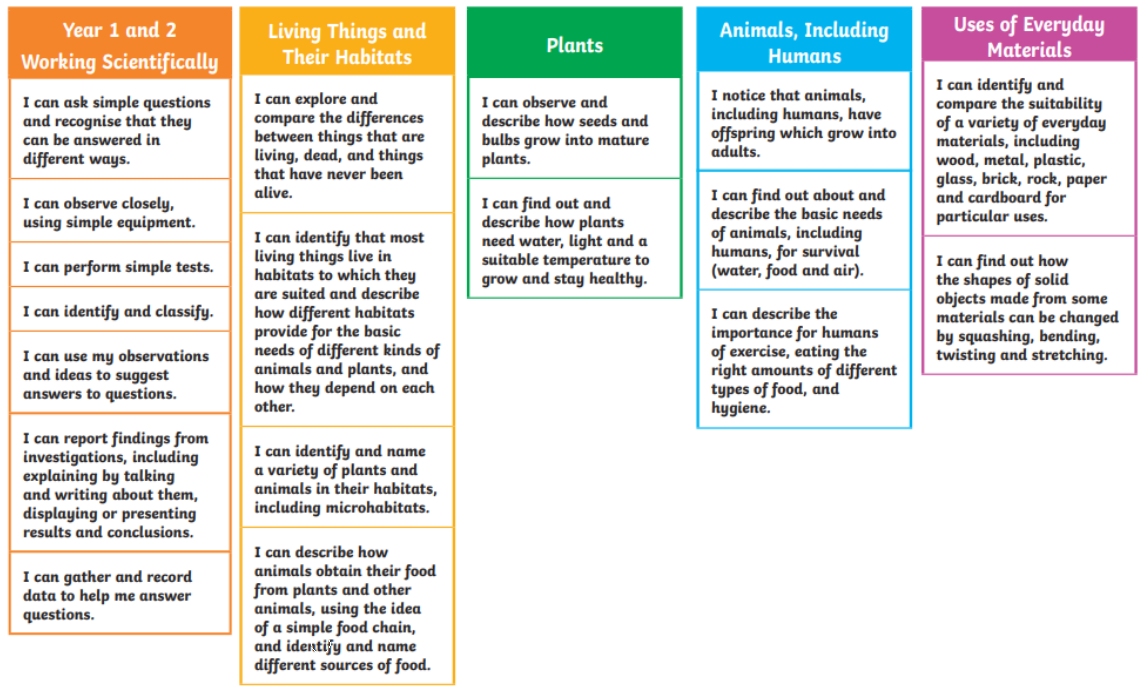
Essential Building Blocks for Year 3
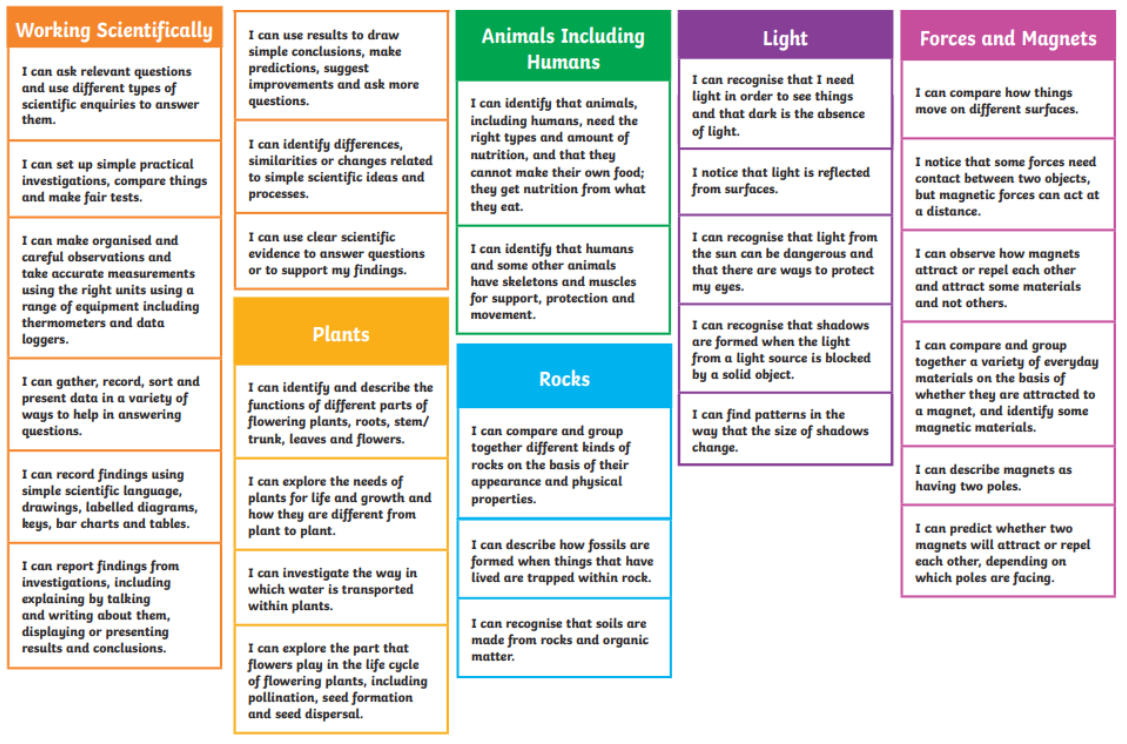
Essential Building Blocks for Year 4
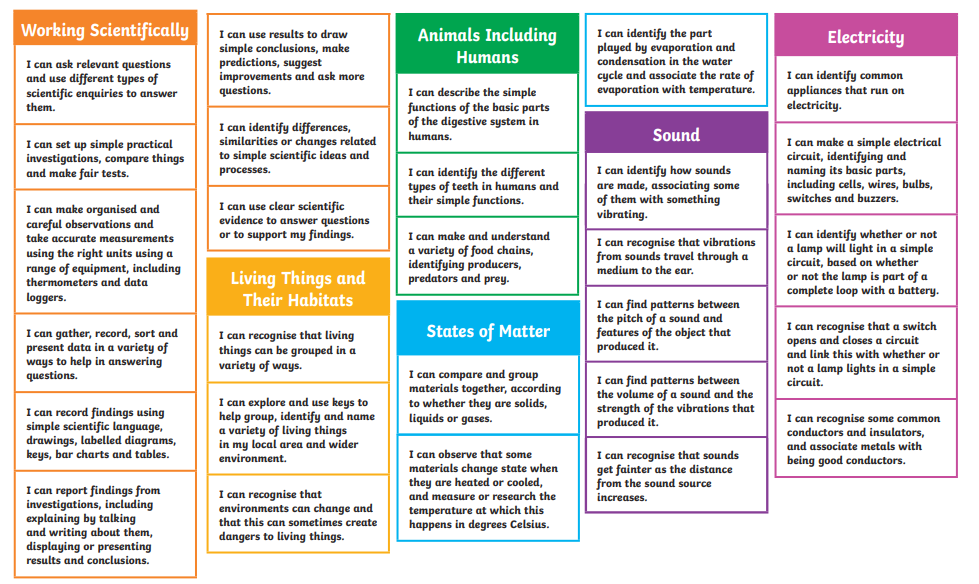
Essential Building Blocks for Year 5
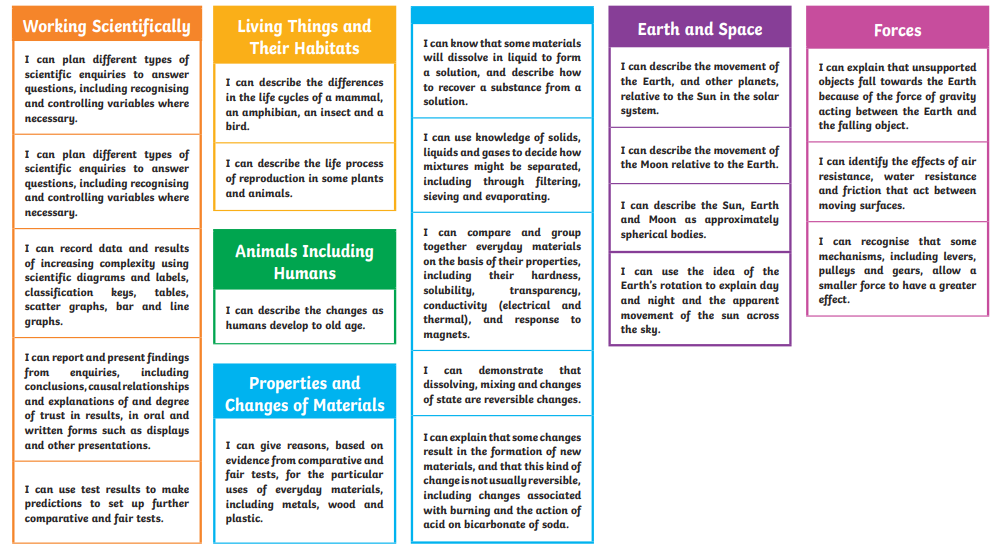
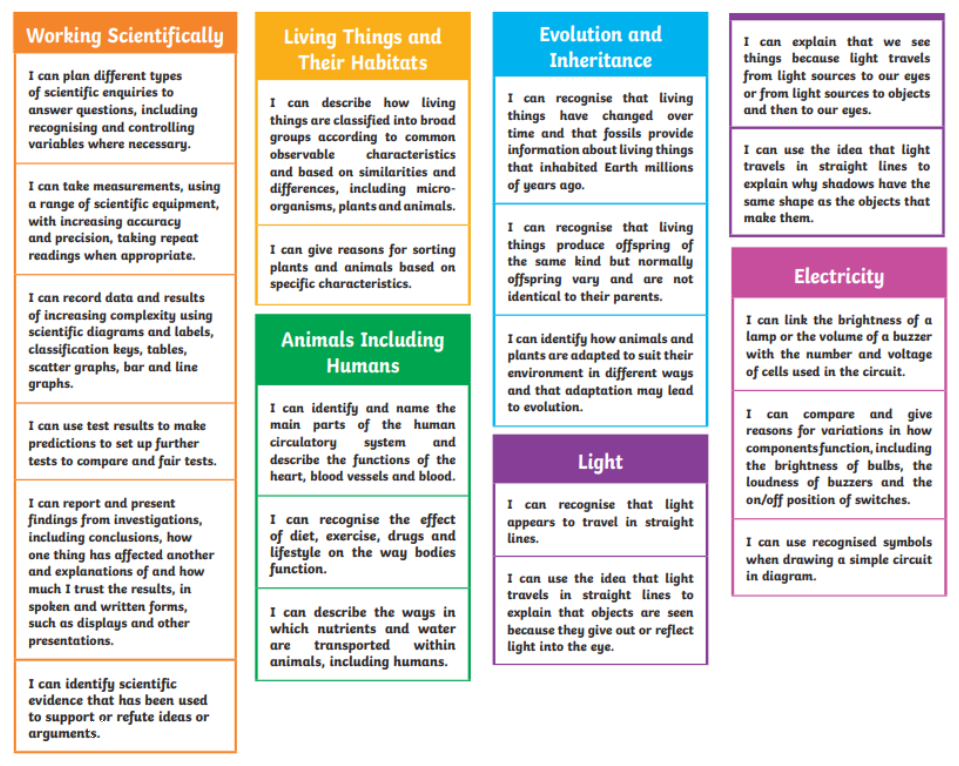
Essential Building Blocks for Year 6
Science Vocabulary
|
Science Topic |
Year 1-2 |
Year 3-4 |
Year 5-6 |
|
Working Scientifically |
Experience, observe, changes, patterns, grouping, sorting, classifying, compare, identify (name), data, measure, record, equipment, questions, test, investigate, explore, magnifying glass / hand lens, same, different |
Develop, enquiry, practical, enquiry, fair test, comparative test, relationships, conclusion, accurate, thermometer, data logger, estimate data, diagram, key, (identifying) table chart, bar chart, results, predictions, explanation, reason, similarity, difference, question, evidence, information, findings, criteria, values, properties, characteristics |
Variables, evidence, justify, accuracy, precision, scatter graphs, bar graphs, line graphs, argument (science), causal, relationship |
|
Animals, including humans |
Names of common animals: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, Mammals, carnivores, herbivores, omnivores Human body senses: see, hear, feel, smell, taste Habitat, local environment, pet, wild, animal, insect, minibeast, food, eat, head, neck, body, arms, legs, ears, eyes, nose, mouth, tongue, hands, feet, fingers, toes, elbows, knees, hair, teeth, grow, healthy, offspring, adults, young, water, air, survive, exercise, hygiene, egg, chick, chicken, caterpillar, pupa, moth, butterfly, tadpole, frog, frog spawn, lamb, sheep, calf, cow, foal, horse |
Nutrition, diet, skeleton, muscles, protection, support, movement, bones, skull, shell, digestive system, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, oesophagus, Types of teeth: molar, premolar, incisor, canine saliva |
Puberty, gestation period, circulatory system, heart, lungs, blood vessels, blood, lifestyle, disease, water transportation, nutrient transportation, oxygen, air, breathing, exercise, diet, drugs |
|
Plants |
Plants, wild plants, garden plants, evergreen trees, deciduous trees, common flowering plants, flowers, vegetables, leaf/leaves, flower, blossom, petal, stem, trunk, branch, root, seed, bulb, bud, growth, grow, habitat, local environment, leaf fall, water, light, temperature, healthy growth, survive, soil, germinate, stages of growth |
Functions, nutrients, nutrition, air, transport (water), life cycle, pollination, seed formation, seed dispersal, reproduce, fertiliser |
|
|
Living things and their habitats (including evolution and inheritance) |
Pond, garden, field, park, woodland, sea shore, river, ocean, forest, rainforest, stones, rocks, logs, leaf, litter, habitat, micro-habitat, living, dead, not living, alive, healthy, food, food chain, depend, source of food, shelter, grow, growth, healthy |
Environment, non-flowering plants, ferns, mosses, flowering plants, grasses, Vertebrate animals: fish, birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles Invertebrate animals: snails, worms, slugs, spiders, insects Human impact – litter, deforestation, population increase, nature reserves |
life cycles, reproduction, life processes, sexual and asexual reproduction (plants), root cuttings, classification, microorganisms, organisms, evolution, evolve, adaptation, variation, inherit, inheritance |
|
Materials (including rocks and soils) |
Everyday materials: wood, paper, plastic, metal, glass, water, rock, brick, stone, fabric material, foil, elastic, dough, rubber, card, cardboard, clay Object: make/made hard/soft shiny/dull stretchy/stiff rough/smooth bendy/not bendy waterproof/not waterproof transparent/opaque absorbent/not absorbent, squash, twist, bend, stretch |
Rock, soil, fossil, organic matter, grains, crystals, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock, igneous rock |
Properties, hardness, solubility, transparency, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, magnetism, dissolve, solution, substance, separating, mixing, filtering, sieving, reversible change, burning, rusting, reactions, irreversible change |
|
States of matter |
|
Solid, liquid, gas, temperature, heat (heating), cool (cooling), water cycle, evaporation, condensation, melting, freezing, |
Solid, liquid, gas, temperature, heat (heating), cool (cooling), water cycle, evaporation, condensation, melting, freezing, |
|
Earth and space (Including Seasons) |
Seasons, seasonal change, spring, summer, autumn, winter, weather, sun, sunshine, rain, snow, sleet, ice, frost, fog, cloud, hot, cold, storm, sky, earth, night, day, |
|
Solar system planets: Mercury, Venus, earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Moon, stars, spherical bodies, rotation, orbit, satellite, gravity, light years |
|
Electricity |
|
Electricity, simple circuit, light bulb, cell, wire, buzzer, switch, motor, battery, series, circuit, conductor, insulator |
Voltage, components, symbols, circuit, diagram |
|
Forces |
|
Move, movement, surfaces, forces, push, pull, contact, distance, magnet, bar magnet, ring magnet, horseshoe magnet, attract, repel, poles (of magnets), magnetic, materials |
Gravity, air resistance, water resistance, friction, levers, pulleys, gears, springs |
|
Light |
|
Light, dark (absence of light), reflect, shadow, opaque, mirror, reflective, surface |
Light sources, periscope |
|
Sound |
|
Sound, vibration, vibrate, pitch, volume, insulation |
|
Science Recommended Reads/ Websites/ Apps
If you love Science, you will love these books! You can find more recommended read at https://home.oxfordowl.co.uk/books-to-inspire-young-scientists/






Science Experiments at home!
- Siemen’s Super Science!
- Science Fun for Everyone!
- 10 Magic Experiments
- 5 Experiments with Grover from Sesame Street (Early Years)
- 10 Easy Experiments for Kids (KS1)
- 20 Easy Home Experiments (KS2)

Science activities! Lots of amazing Science activities can be found by following these links:
- British Science Association CREST awards (Stars for 5-7, Superstars for 7-11)
- Explorify – Wellcome Trust online activities to make you think! (Dr Jo is an Explorify Champion so just ask if you have any questions)
- Great Bug Hunt
- RSPB Bird watch (has closed but you can still ID birds!) and wild challenges
- Nature Detectives – special school closure activities from The Woodland Trust
- Kew Gardens Learning at home resources
- RHS Gardening activities
- Cambridge University Botanic Gardens downloadable resources for families
- Wildlife Trust activities for families
- Practical Action Schools – investigations to get your teeth into (older children)
- National trust 50 Things to do before you’re 11 3/4
- The Scouts The Great Indoors activities
- Wallace And Gromit Cracking Ideas – have a go at inventing
- Starters for STEM 10 minute activities from STEM Learning
- NASA kids club
- AstroScience Challenge launches 27th April
- ExpeRImental from The Royal Institution
- Train like an Astronaut – PE and science activities
- Institute of Physics (IOP) Marvin and Milo STEM cartoon activities
- Ogden Trust Physics Home Learning
- Have a go at coding
- Science with Minecraft

GoodrichChurch of England Primary School
Contact Us
Ross-on-Wye, Herefordshire, HR9 6HY